Manufacturing recycled fabric: an eco-responsible approach
Share
Now that environmental protection is becoming a priority, the textile industry is increasingly turning to sustainable solutions. Manufacturing recycled fabrics is one of these initiatives that helps reduce our environmental impact. But how is recycled fabric made, and why is it so important?
Textile recycling: a response to overproduction
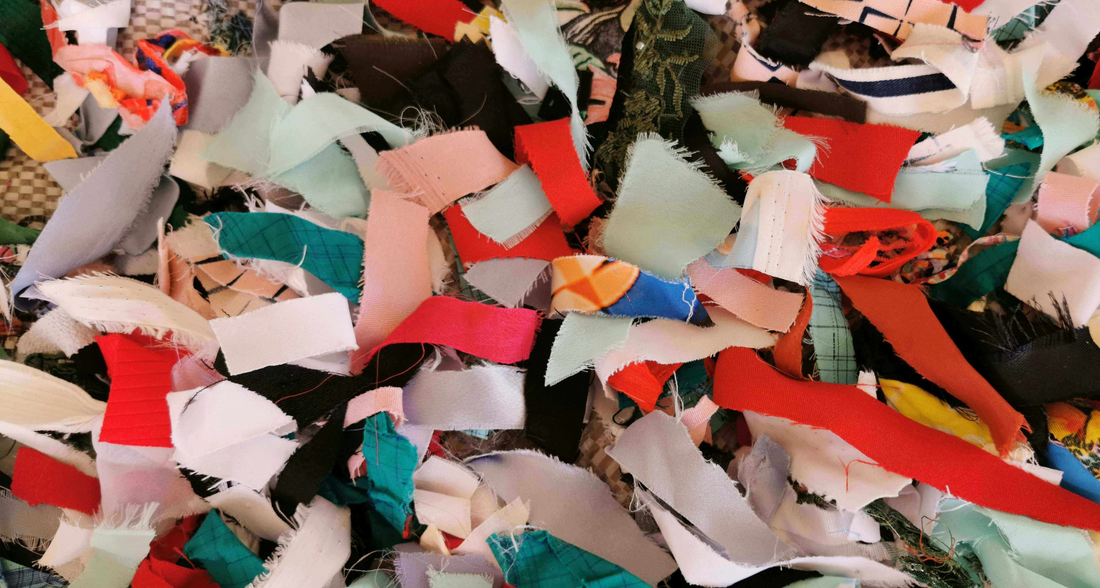
As we already know, the fashion industry is one of the most polluting in the world, with billions of tons of clothing produced each year. Many of these textiles end up in landfills or are incinerated. In response to this overproduction, textile recycling has become a major issue. Recycling fabrics reduces the demand for new raw materials and limits waste.
The process of making recycled fabric
The manufacturing of recycled fabric begins with the collection of raw materials. These materials can come from various sources:

Used clothing: end-of-life clothing is collected to be transformed into new fibers.
Production scraps: fabric scraps from the manufacture of clothing or other textile products are collected for recycling.
Industrial waste: fibers from industry can also be used.
Once the raw materials are collected, they go through several processing stages:
Sorting and selection: Clothing and textiles are sorted according to their composition (cotton, polyester, wool, etc.). This ensures that the materials are suitable for recycling together.
Shredding and shredding: Textiles are shredded into small fibers. This process separates the threads and creates a raw material ready for processing.
Spinning: The recycled fibers are then spun to create new yarns. This step is crucial because it determines the quality of the final fabric.
Weaving or knitting: The threads are finally woven or knitted to form the recycled fabric, ready to be used in the manufacture of new clothing or products.
The benefits of recycled fabrics
Reducing the ecological footprint: by using recycled fibers, we reduce the consumption of water, energy and natural raw materials such as cotton or oil (for synthetic fibers).
Reduced waste: Fewer textiles end up in landfills or are incinerated, helping to combat pollution.
Fewer chemicals: The recycling process generally requires fewer chemicals than producing new fabrics, which helps limit the release of harmful substances.
The challenges to be met
Despite its many benefits, textile recycling also presents some challenges. Recycled fibers are sometimes less durable than new fibers, which can affect the durability of clothing. Additionally, production costs can be higher due to complex processing. Finally, not all textiles can be recycled indefinitely; after a few cycles, the quality of the fibers can deteriorate.
A promising future for recycled fabric
Demand for recycled textiles is constantly increasing, thanks in part to consumer awareness of the importance of sustainable development. Furthermore, technological innovations are improving the quality and diversity of recycled fabrics. The future of the textile industry therefore lies, in part, in its ability to more systematically integrate recycling into its production processes.
In conclusion, manufacturing recycled fabric represents a major step forward for the textile industry. While not without its challenges, this approach helps reduce our ecological footprint while meeting a growing demand for more environmentally friendly products. As a consumer, choosing clothing made from recycled materials is a simple yet effective way to help protect our planet.